Recent Articles
-
Christmas Sword Buying Guide 2025
Dec 03, 25 10:53 PM
Japanese Sword Training Basics
Japanese sword training is something of a lifelong journey. Even the masters consider themselves to be humble students, constantly striving for perfection and always feeling that they can execute a cut cleaner, faster and with more precision...
As such, even the basics are subject to continual refinement, and it is most definitely a journey best started with proper instruction under the watchful eye of a qualified teacher.
Yet for those who are curious as to what to expect in a JSA (Japanese Sword Art) dojo, or others with a purely academic interest, this article is at the very least, a tentative introduction to the mindsets and training methodologies of the arts as a whole...
Ritualism and Dojo Etiquette
One thing you will notice about traditional Japanese swordsmanship is the emphasis on ritual and Etiquette.
Partially this is done for safety reasons (after all, its stands to reason that a dojo full of sword wielding students can be a dangerous place to be!) and partially it is done to cultivate the right spirit of respect and reverence for the art and the sword itself.
While each school and each style does it a little differently, almost all start out with the class lined up (with the most senior students at the front, to the most junior at the back) facing the Sensei. Before the class begins in earnest, they transfer the sword from the left hand to the right (symbolizing their intention in the dojo is one of peace and learning, as they cannot attack while holding the sword in the right hand) before bowing and attaching the sword to their belt as shown in the video below.
VIDEO: Bowing In Ceremony
Highly formalized and steeped in tradition, the bowing in ceremony is all about respect.
In a similar way, once a Japanese sword training session is completed (with most modern dojos running from around 1 to 2 hours per class) the ritual is more or less reversed.
Each school will have many additional rules that apply before, during and after training. While these rituals may chafe to the Western student at first, everything not matter how obscure it may seem is done for a reason in the Japanese sword arts.
Some of these rules are designed to show that your intent in the training hall is to learn and to avoid behavior which is threatening or dangerous. Others are aimed at cultivating the correct mindset to build a solid foundation of humility and openness (once you think Im so good at this! youve instantly stopped learning and are in fact doing yourself a disservice).
To discard any elements is to miss out on cultivating the martial spirit of swordsmanship that is central to attaining true mastery.
Basic Cutting Techniques
What follows are some of the basic cuts that form the building blocks of Japanese sword training.
Again, each style is different. Some start with the sword further back than others, some finish with it closer to the ground. None are wrong just different approaches to achieving the same result...
In traditional Japanese sword training, these techniques are often practiced many thousands of times before any degree of proficiency is obtained, which is why it is important to get proper instruction as practicing them solo without a sensei to instruct you can ingrain some seriously bad habits that will take years to untrain.
However, with that in mind, from an academic point of view, here are three of generic cutting techniques.
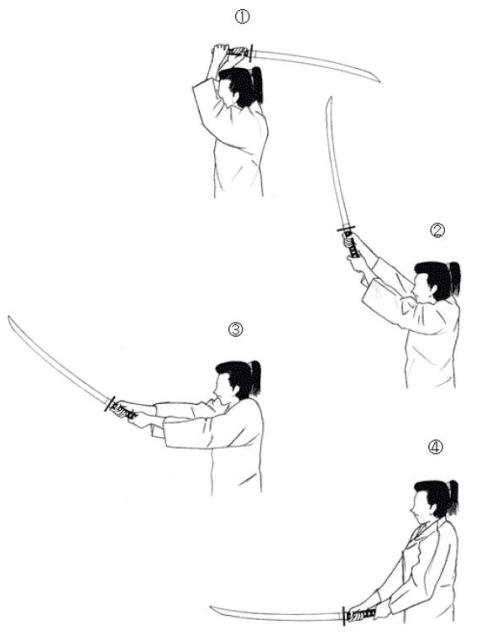
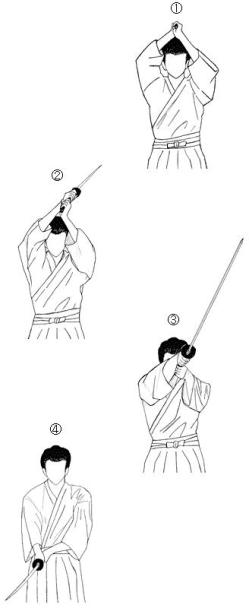
This is the most basic, yet fundamental Japanese sword training cut. From (1) an overhead position, with the sword perfectly horizontal (check in the mirror to make sure) it is (2) cast out, much like casting a fishing rod by pulling with the left hand at the bottom, much like a lever until (3) it makes contact with the head or shoulder of the opponent and then (4) simply drops down to stop horizontally again. The action should be done without power, allowing the blade to drop down.
A common mistake is to use too much force in the right hand, which is really only just guiding the blade. One way to minimize this is to practice the casting movement holding the sword in the left hand only.
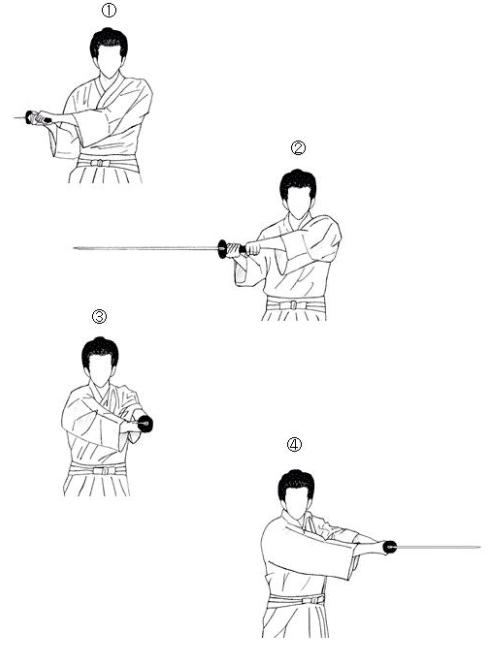
Much like the basic swing the blade begins (1) facing out horizontally behind you and is (2) levered by the left hand, arcing out with the (3) cut making contact with the target and (4) cutting through the other side.
A vertical cut to the right side of the shoulder (and out through the left armpit) it (1) begins in the same position as the basic overhead cut and (2) then tilts slightly on a diagonal path as it is levered by the left hand.
With the feeling of casting a fishing line it (3) makes contact with the target as the arms are extended and the momentum (4) carries through the target, finishing in a position slightly slower than horizontal, breaking with the elbows touching the body.
Again, be sure not to power it with the right hand but let speed and the weight of the blade do all the work.
This is a very important point to remember whenever you do Japanese sword training - and you will notice the difference from an overly strong technique and a correct one by the sound it makes as it cuts through the air...
Putting it all Together
he core of Japanese sword training is undoubtedly the ritualistic patterns known as Kata (forms). These vary from school to school, but all the major categories of Japanese sword training arts Iaido, Kenjutsu and Kendo have them to some degree or another.
Contained within these seemingly archaic movements are many lethal techniques that, ideally at least, are based on tried and tested combat techniques. (It has been argued that some schools are more pure than others, with some supposedly being diluted during Japans long period of domestic peace though the frequency of duels between Samurai would suggest that truly ineffectual arts would not have been passed down through the generations, natural attrition would take care of that!).
Most sword schools start the beginning student off with very simple Kata.
In the case of iaido the first few kata are often no more than drawing the sword, delivering a single strike and then re-sheathing it. While on the one hand, these sword training methods were designed to be practical, training the swordsman by building the fluid and economical movements deep into muscle memory with continual repetition they also served a greater purpose to develop Mushin or single minded, unwavering focus so that the warriors mind would be clear, even in the face of death...
Below is a video showing one such beginning Kata.
VIDEO: A Basic Iaido Kata (form)
Zanshin: focusing 100% from beginning to end.
The beauty of Kata like these is that this is one form of Japanese sword training you can practice by yourself, anywhere and anytime. But that said, it is extremely important at all times when performing a single person Kata to strongly visualize your opponent and where they are in relation to your techniques, otherwise your Kata will take on the characteristics (and spirit) of a mere dance...
Kenjutsu schools tend take a different approach. Most of their Kata are partnered exercises, starting very simple as shown in the video below.
VIDEO: A Basic Kenjutsu Kata (form)
A series of Kata drills for Kenjutsu with Shihan James Williams
While there is some crossover between the Iaido and Kenjutsu schools, it is reasonable to say that Iaido has an emphasis on solo kata while Kenjutsu has a stronger emphasis on partnered exercises.
Again, learning the Kata is really something that should be left to the
dojo, however there are some high quality instructional DVDs and Books
on the market that while they cannot surpass the kind of Japanese sword
training available in the dojo are a valid alternative for those who
are casually interested, or where geography makes practical instruction
an impossibility.
Free Sparring
It should come as no big surprise that free sparring with live blades is not a part of Japanese sword training, though at the highest levels, Masters perform partnered exercises with razor sharp live blade Shinken (Katana made in Japan using traditional techniques).
In Kenjutsu, once the basic Kata have been mastered to a high level, high level students may begin introducing additional techniques into their partnered Japanese sword training Kata which can become so fluid it is, for all intents and purposes, free sparring.
And within some schools free sparring is developed with heavily padded bokken known as fukuro shinai. However, the style of Japanese sword training that truly specializes in free sparring is Kendo.
While beginning Kendo students focus a lot of their energies on developing basic techniques, footwork, and partnered Kata with the Shinai (bamboo sword) the aim of their training is to develop the skills required for free sparring and serious competition.
VIDEO: Kendoka's amazing reaction times
This video shows some almost superhuman reaction times in slow motion. Amazing.
On the downside, Kendo is much more of a sport than a martial art per se, and the wrist flicking strikes employed can create bad habits for Japanese sword training with a shinken (live blade) or iaito though one the other side, it does indeed cultivate a strong warrior spirit and is most certainly a test of skill (for more information on Kendo, visit KendoKorner.com). As such, I have heard it said that to be a well balanced swordsman, cross training between the various styles is strongly encouraged.
Indeed, one style that seeks to re-integrate the various somewhat fragmented Japanese sword schools together is Toshishiro Obata's Shinkendo School.
With a syllabus of Japanese sword training methods more akin to those practiced by the Samurai it emphasizes:
- Suburi (cutting exercises)
- Battoho (drawing techniques)
- Kata (Forms)
- Tachiuchi (Sparring)
- And Tameshigiri (test cutting)
As such, it could be argued that this modern day swordmaster (who is a personal hero of mine since boyhood) is contributing to the evolution and reconstruction of the ancient Japanese sword training techniques.
FREE PDF EBOOK FROM SBG!
FREE JAPANESE SWORD TRAINING EBOOK
Japanese Sword Arts 101 has been written as a very basic introduction to the Japanese sword arts.
Containing examples of the etiquette, basic techniques and more, this short and to the point PDF ebook is a great starting point and best of all, its totally free.
I hope this information on Japanese Sword Training has been helpful. To return to Sword Fighting and Training Basics from Japanese Sword Training Basics, click here
Buying Swords Online Can Be DANGEROUS!
Find the Best Swords in the:
Popular & Recommended ARTICLES

The ONLY true free online magazine for sword enthusiasts. Delivered once a month on the 1st day of the month, no filler and no BS, just the latest sword news & info delivered straight to your inbox.













